Check inputs to java.util.ZipInputStream for cases that cause consumption of excessive system resources. Denial of service can occur when resource usage is disproportionately large in comparison to the input data that causes the resource usage. The nature of the zip algorithm permits the existence of "zip bombs" whereby where a short small file is very highly compressed, such as ZIPs, GIFs, and gzip-encoded HTTP content consumes excessive resources when uncompressed because of extreme compression.
| Wiki Markup |
|---|
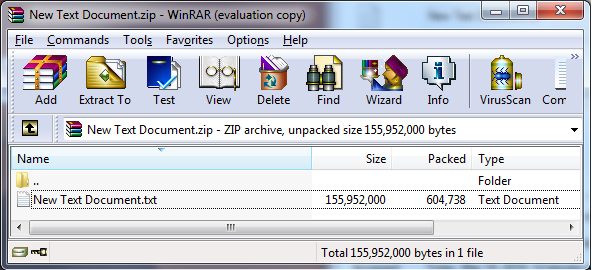
The zip algorithm is capable of producing very large compression ratios \[[Mahmoud 2002|AA. Bibliography#Mahmoud 02]\]. The example belowFigure 2-1 shows a file that was compressed from 148MB to 590KB, a ratio of more than 200 to 1. The file consists of arbitrarily repeated data: alternating lines of '_a'_ characters and '_b'_ characters. Even higher compression ratios can be easily obtained using input data that is targeted to the compression algorithm, or using more input data (that is untargeted), or other compression methods. |
Any entry in a Zip zip file whose uncompressed file size is beyond a certain limit must not be uncompressed. The actual limit is dependent on the capabilities of the platform.
This rule is a specific instance of the more general rule MSC05-J. Do not assume infinite heap space.
Noncompliant Code Example
...
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
static final int BUFFER = 512; // ... // external data source: filename BufferedOutputStream dest = null; FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(filename); ZipInputStream zis = new ZipInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(fis)); ZipEntry entry; while ((entry = zis.getNextEntry()) != null) { System.out.println("Extracting: " + entry); int count; byte data[] = new byte[BUFFER]; // write the files to the disk FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(entry.getName()); dest = new BufferedOutputStream(fos, BUFFER); while ((count = zis.read(data, 0, BUFFER)) != -1) { dest.write(data, 0, count); } dest.flush(); dest.close(); } zis.close(); |
...
Related Guidelines
CWE-409, ". Improper Handling of Highly Compressed Data (Data Amplification)" handling of highly compressed data (data amplification) | |
Secure Coding Guidelines for the Java Programming Language, Version 3.0 | Guideline 2-5. Check that inputs do not cause excessive resource consumption |
...
<ac:structured-macro ac:name="unmigrated-wiki-markup" ac:schema-version="1" ac:macro-id="4bd3bafbbbd76846-a62a7fd4-422e439d-86448491-503d175c91ef1b79c038e6d6"><ac:plain-text-body><![CDATA[ | [[Mahmoud 2002 | AA. Bibliography#Mahmoud 02]] | [Compressing and Decompressing Data Using Java APIs | http://java.sun.com/developer/technicalArticles/Programming/compression/] | ]]></ac:plain-text-body></ac:structured-macro> |
...