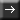
The C++ Standard, [stmt.return], paragraph 2 [ISO/IEC 14882-2014], states the following:
Flowing off the end of a function is equivalent to a
returnwith no value; this results in undefined behavior in a value-returning function.
A value-returning function must return a value from all code paths; otherwise, it will result in undefined behavior. This includes returning through less-common code paths, such as from a function-try-block, as explained in the C++ Standard, [except.handle], paragraph 15:
Flowing off the end of a function-try-block is equivalent to a
returnwith no value; this results in undefined behavior in a value-returning function (6.6.3).
Noncompliant Code Example
In this noncompliant code example, the programmer forgot to return the input value for positive input, so not all code paths return a value.
int absolute_value(int a) {
if (a < 0) {
return -a;
}
}
Compliant Solution
In this compliant solution, all code paths now return a value.
int absolute_value(int a) {
if (a < 0) {
return -a;
}
return a;
}
Noncompliant Code Example
In this noncompliant code example, the function-try-block handler does not return a value, resulting in undefined behavior when an exception is thrown.
#include <vector>
std::size_t f(std::vector<int> &v, std::size_t s) try {
v.resize(s);
return s;
} catch (...) {
}
Compliant Solution
In this compliant solution, the exception handler of the function-try-block also returns a value.
#include <vector>
std::size_t f(std::vector<int> &v, std::size_t s) try {
v.resize(s);
return s;
} catch (...) {
return 0;
}
Exceptions
MSC54-CPP-EX1: Flowing off the end of the main() function is equivalent to a return 0; statement, according to the C++ Standard, [basic.start.main], paragraph 5 [ISO/IEC 14882-2014]. Thus, flowing off the end of the main() function does not result in undefined behavior.
MSC54-CPP-EX2: It is permissible for a control path to not return a value if that code path is never expected to be taken and a function marked [[noreturn]] is called as part of that code path or if an exception is thrown, as is illustrated in the following code example.
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
[[noreturn]] void unreachable(const char *msg) {
std::cout << "Unreachable code reached: " << msg << std::endl;
std::exit(1);
}
enum E {
One,
Two,
Three
};
int f(E e) {
switch (e) {
case One: return 1;
case Two: return 2;
case Three: return 3;
}
unreachable("Can never get here");
}
Risk Assessment
Failing to return a value from a code path in a value-returning function results in undefined behavior that might be exploited to cause data integrity violations.
Rule | Severity | Likelihood | Remediation Cost | Priority | Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MSC52-CPP | Medium | Probable | Medium | P8 | L2 |
Automated Detection
Tool | Version | Checker | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Astrée | 22.10 | return-implicit | Fully checked |
| Axivion Bauhaus Suite | 7.2.0 | CertC++-MSC52 | |
| Clang | 3.9 | -Wreturn-type | Does not catch all instances of this rule, such as function-try-blocks |
| CodeSonar | 8.1p0 | LANG.STRUCT.MRS | Missing return statement Non-void noreturn, |
| Helix QAC | 2024.2 | DF2888 | |
| Klocwork | 2024.2 | FUNCRET.GEN FUNCRET.IMPLICIT | |
| LDRA tool suite | 9.7.1
| 2 D, 36 S | Fully implemented |
| Parasoft C/C++test | 2023.1 | CERT_CPP-MSC52-a | All exit paths from a function, except main(), with non-void return type shall have an explicit return statement with an expression |
| Polyspace Bug Finder | R2024a | CERT C++: MSC52-CPP | Checks for missing return statements (rule partially covered) |
| SonarQube C/C++ Plugin | 4.10 | S935 | |
| PVS-Studio | 7.31 | V591 | |
| RuleChecker | 22.10 | return-implicit | Fully checked |
Related Vulnerabilities
Search for vulnerabilities resulting from the violation of this rule on the CERT website.
Bibliography
| [ISO/IEC 14882-2014] | Subclause 3.6.1, "Main Function" |